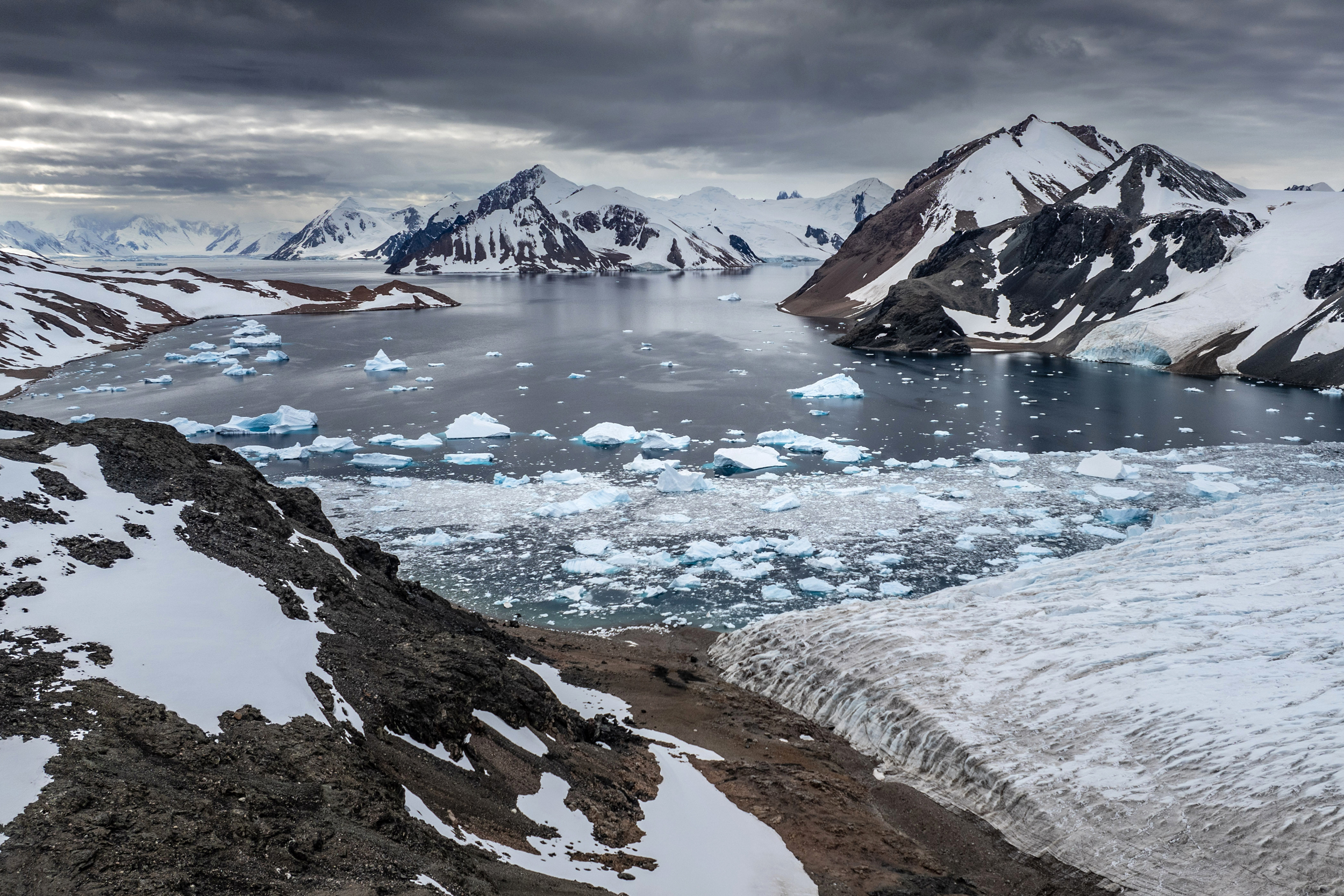
As recently as the 1990s, when the Greenland Ice Sheet and the rest of the Arctic region were measurably thawing under the climatic blowtorch of human-caused global warming, most of Antarctica’s vast ice cap still seemed securely frozen.
But not anymore. Physics is physics. As the planet heats up, more ice will melt at both poles, and recent research shows that Antarctica’s ice caps, glaciers and floating ice shelves, as well as its sea ice, are just as vulnerable to warming as the Arctic.
Both satellite data and field observations in Antarctica reveal alarming signs of a Greenland-like meltdown, with increased surface melting of the ice fields, faster-moving glaciers and dwindling sea ice. Some scientists are sounding the alarm, warning that the rapid “Greenlandification” of Antarctica will have serious consequences, including an accelerated rise in sea levels and significant shifts in rainfall and drought patterns.
The Antarctic ice sheet covers about 5.4 million square miles, an area larger than Europe. On average, it is more than 1 mile thick and holds 61 percent of all the fresh water on Earth, enough to raise the global average sea level by about 190 feet if it all melts. The smaller, western portion of the ice sheet is especially vulnerable, with enough ice to raise sea level more than 10 feet.
Thirty years ago, undergraduate students were told that the Antarctic ice sheets were going to be stable and that they weren’t going to melt much, said Ruth Mottram, an ice researcher with the Danish Meteorological Institute and lead author of a new paper in Nature Geoscience that examined the accelerating ice melt and other similarities between changes in northern and southern polar regions.
“We thought it was just going to take ages for any kind of climate impacts to be seen in Antarctica. And that’s really not true,” said Mottram, adding that some of the earliest warnings came from scientists who saw collapsing ice shelves, retreating glaciers and increased surface melting in satellite data
One of the early warning signs was the rapid collapse of an ice shelf along the narrow Antarctic Peninsula, which extends northward toward the tip of South America, said Helen Amanda Fricker, a geophysics professor with the Scripps Institute of Oceanography Polar Center at the University of California, San Diego.
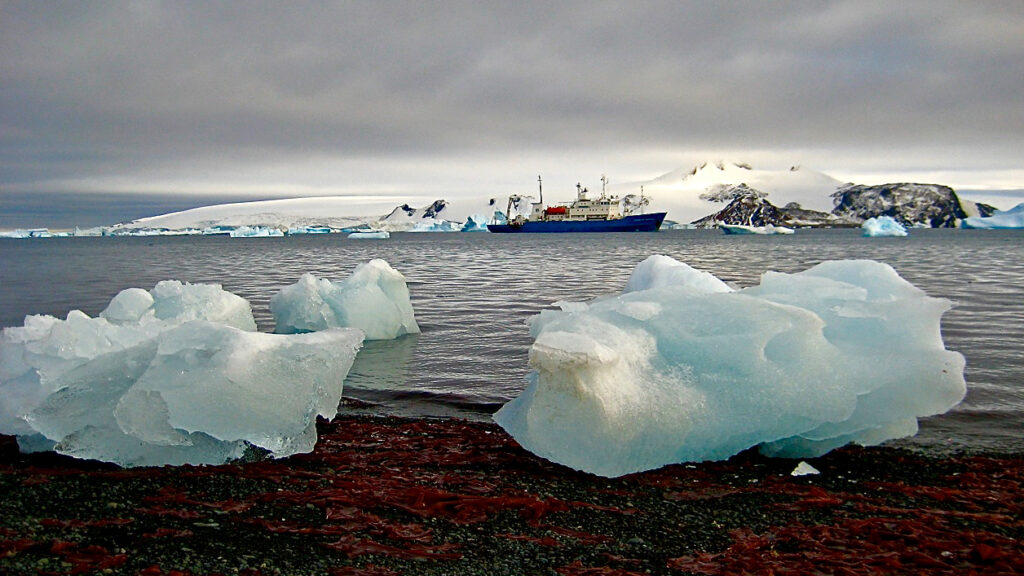

After a string of record-warm summers riddled the floating Rhode Island-sized slab of ice with cracks and meltwater ponds, it crumbled almost overnight. The thick, ancient ice dam was gone, and the seven major outlet glaciers behind it accelerated toward the ocean, raising sea levels as their ice melted.
“The Larsen B ice shelf collapse in 2002 was a staggering event in our community,” said Fricker, who was not an author of the new paper. “We just couldn’t believe the pace at which it happened, within six weeks. Basically, the ice shelves are there and then, boom, boom, boom, a series of melt streams and melt ponds. And then the whole thing collapsed, smattered into smithereens.”
Glaciologists never thought that events would happen that quickly in Antarctica, she said.
Same Physics, Same Changes
Fricker said glaciologists thought of changes in Antarctica on millennial timescales, but the ice shelf collapse showed that extreme warming can lead to much more rapid change.
Current research focuses on the edges of Antarctica, where floating sea ice and relatively narrow outlet glaciers slow the flow of the ice cap toward the sea. She described the Antarctic Ice Sheet as a giant ice reservoir contained by a series of dams.
“If humans had built those containment structures,” she said, “we would think that they weren’t very adequate. We are relying on those dams to hold back all of that ice, but the dams are weakening all around Antarctica and releasing more ice into the ocean.”
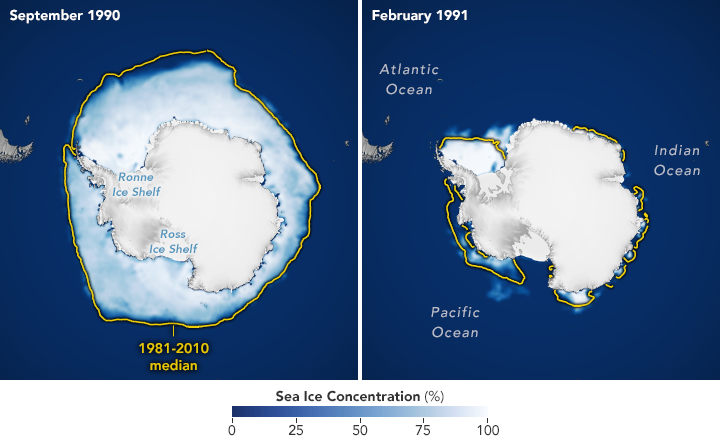
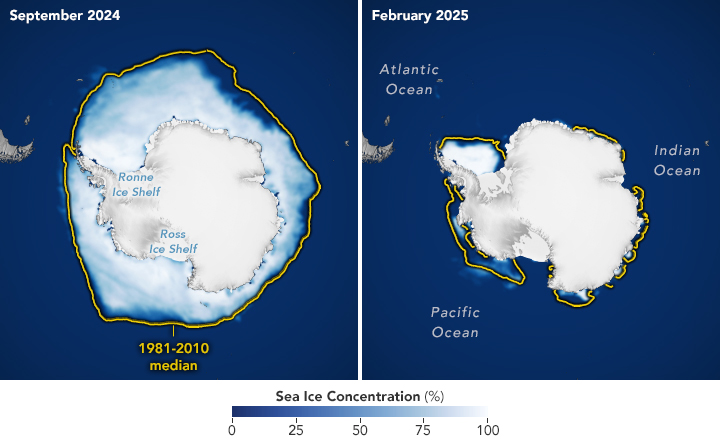
The amount of ice that’s entered the ocean has increased fourfold since the 1990s, and she said, “We’re on the cusp of it becoming a really big number … because at some point, there’s no stopping it anymore.”
The Antarctic Ice Sheet is often divided into three sectors: the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, the largest and thickest; the West Antarctic Ice Sheet; and the Antarctic Peninsula, which is deemed the most vulnerable to thawing and melting.
Mottram, the new paper’s lead author, said a 2022 heatwave that penetrated to the coldest interior part of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet may be another sign that the continent is not as isolated from the rest of the global climate system as once thought. The extraordinary 2022 heatwave was driven by an atmospheric river, or a concentrated stream of moisture-laden air. Ongoing research “shows that there’s been an increase in the number of atmospheric rivers and an increase in their intensity,” she said.
This story is funded by readers like you.
Our nonprofit newsroom provides award-winning climate coverage free of charge and advertising. We rely on donations from readers like you to keep going. Please donate now to support our work.
Donate NowAntarctica is also encircled by a powerful circumpolar ocean current that has prevented the Southern Ocean from warming as quickly as other ocean regions. But recent climate models and observations show the buffer is breaking down and that relatively warmer waters are starting to reach the base of the ice shelves, she said.
New maps detailing winds in the region show that “swirls of air from higher latitudes are dragging in all the time, so it’s not nearly as isolated as we always told when we were students,” she said.
Ice researcher Eric Rignot, an Earth system science professor at the
University of California, Irvine, who did not contribute to the new paper, said via email that recent research on Antarctica’s floating ice shelves emphasizes the importance of how the oceans and ice interact, a process that wasn’t studied very closely in early Greenland research. And Greenland shows what will happen to Antarctic glaciers in a warmer climate with more surface melt and more intense ice-ocean interactions, he added.
“We learn from both but stating that one is becoming the other is an oversimplification,” he said. “There is no new physics in Greenland that does not apply to Antarctica and vice versa.”
Rignot said the analogy between the two regions also partly breaks down because Greenland is warming up at two to three times the global average, “which has triggered a slowing of the jet stream,” with bigger wobbles and “weird weather patterns” in the Northern Hemisphere.
Antarctica is warming slightly less than the global average rate, according to a 2025 study, and the Southern Hemisphere jet stream is strengthening and tightening toward the South Pole, “behaving completely opposite,” he said.
Mottram said her new paper aims to help people understand that Antarctica is not as remote or isolated as often portrayed, and that what happens there will affect the rest of the global climate system.
“It’s not just this place far away that nobody goes to and nobody understands,” she said. “We actually understand quite a lot of what’s going on there. And so I also hope that it drives more urgency to decarbonize, because it’s very clear that the only way we’re going to get out of this problem is bringing our greenhouse gases down as much as possible, as soon as possible.”
About This Story
Perhaps you noticed: This story, like all the news we publish, is free to read. That’s because Inside Climate News is a 501c3 nonprofit organization. We do not charge a subscription fee, lock our news behind a paywall, or clutter our website with ads. We make our news on climate and the environment freely available to you and anyone who wants it.
That’s not all. We also share our news for free with scores of other media organizations around the country. Many of them can’t afford to do environmental journalism of their own. We’ve built bureaus from coast to coast to report local stories, collaborate with local newsrooms and co-publish articles so that this vital work is shared as widely as possible.
Two of us launched ICN in 2007. Six years later we earned a Pulitzer Prize for National Reporting, and now we run the oldest and largest dedicated climate newsroom in the nation. We tell the story in all its complexity. We hold polluters accountable. We expose environmental injustice. We debunk misinformation. We scrutinize solutions and inspire action.
Donations from readers like you fund every aspect of what we do. If you don’t already, will you support our ongoing work, our reporting on the biggest crisis facing our planet, and help us reach even more readers in more places?
Please take a moment to make a tax-deductible donation. Every one of them makes a difference.
Thank you,













